Authenticity vs Integrity Cybersecurity: Everything You Need to Know
When people think about cybersecurity, they often focus on confidentiality, keeping sensitive information private. However, two equally critical aspects are frequently misunderstood or overlooked: authenticity and integrity.
As data breaches, phishing attacks, and software tampering become increasingly common, understanding the difference between these two terms is not just a matter of theory; it’s a foundation for building trust and resilience in any digital environment.
Within the classic CIA Triad of cybersecurity, Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability, integrity is a well-established pillar. But in 2024 and beyond, authenticity has taken center stage as a practical extension of integrity, especially as regulatory frameworks evolve and cyberattacks become more deceptive.
This article breaks down the difference between authenticity vs integrity cybersecurity, using real-world examples, cryptographic practices, and their role in compliance and digital trust. By the end, you’ll understand why both are essential for protecting not just your data, but also your reputation and users.
If you’re ready to take the next step in your tech career journey, cybersecurity is the simplest and high-paying field to start from. Apart from earning 6-figures from the comfort of your home, you don’t need to have a degree or IT background. Schedule a one-on-one consultation session with our expert cybersecurity coach, Tolulope Michael TODAY! Join over 1000 students in sharing your success stories.

RELATED ARTICLE: What Is Integrity in Cybersecurity?
What is Integrity in Cybersecurity?
Integrity in cybersecurity means ensuring that data remains accurate, complete, and unaltered during storage, processing, or transmission. It guarantees that information is not modified, either accidentally or maliciously, without proper authorization.
Why Integrity Matters
Imagine you’re working with financial records or health data. If even a single digit is changed, whether due to a system error or a cyberattack, the consequences can be severe: incorrect diagnoses, financial fraud, or regulatory violations. That’s why ensuring data integrity is a fundamental part of any cybersecurity strategy.
Real-World Examples of Integrity in Action
- Checksums and Hash Functions: Tools like SHA-256 or MD5 generate a unique digital fingerprint of a file. If the file changes in any way, the hash will not match, alerting you to tampering.
- Log Files and Audit Trails: Organizations track all data modifications. If someone tries to change data without permission, these logs help detect it.
- File Integrity Monitoring (FIM): Security tools automatically scan systems to ensure files remain unchanged. If an unauthorized change is detected, alerts are triggered.
These are concrete integrity in cybersecurity measures that protect businesses from manipulation, data loss, and compliance issues.
What is Authenticity in Cybersecurity?

Authenticity in cybersecurity is the assurance that users, systems, or data sources are genuinely who or what they claim to be. It focuses on verifying the identity of entities and the origin of information to prevent deception, impersonation, or spoofing.
How Authenticity Works
When a user logs in or a system receives a file, authenticity checks confirm:
- The user or device is legitimate.
- The data or file originated from a trusted and verified source.
This process is vital in preventing attacks where malicious actors pose as trusted sources to deliver harmful content.
Practical Examples
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Ensures that only verified users can access systems.
- Digital Signatures: Validate that a document or file was created by a recognized sender and has not been altered.
- Code Signing Certificates: Used by software developers to certify that their applications are genuine.
Non-Repudiation and Trust
Authenticity also supports non repudiation in cybersecurity, meaning a sender cannot deny having sent a message or file. Digital signatures play a major role here, providing cryptographic proof of authorship and ensuring accountability.
Why It Matters
Without authenticity, attackers can impersonate trusted users or systems, leading to data breaches, supply chain attacks, and malware infections. Authenticity protects not just data but the trust relationships between users, systems, and organizations.
READ MORE: What Is an ATO in Cybersecurity?
Authenticity vs Integrity: What’s the Difference?

Although authenticity and integrity are closely related in cybersecurity, they serve distinct purposes, and understanding the difference is critical for designing effective security systems.
Core Difference
- Integrity ensures that data has not been altered.
- Authenticity ensures that data comes from a trusted source.
In simple terms:
You can have integrity without authenticity (the data wasn’t changed, but you don’t know who sent it).
But you cannot have authenticity without integrity (if data has been altered, it’s no longer authentic).
Real-World Examples
- A software update file might pass an integrity check (hash matches), but if it comes from an unknown source, authenticity fails, you cannot trust it.
- An email may be digitally signed (authentic), but if its content has been tampered with en route, integrity is broken.
These authenticity vs integrity cybersecurity examples show that both must work together to ensure total trust.
Quick Comparison Table
| Aspect | Integrity | Authenticity |
| Main Goal | Prevent unauthorized changes | Prevent impersonation/spoofing |
| Verification Methods | Checksums, Hashes | Digital Signatures, Certificates |
| Can Exist Independently? | Yes | No (relies on integrity) |
| Example | Verify file is unchanged | Verify file is from Microsoft |
| Keyword Usage | Integrity in cybersecurity | What is authenticity in cyber security |
Together, these elements ensure data is both untampered and trustworthy, a dual requirement in any secure system.
SEE ALSO: What Is Redundancy in Cybersecurity? A Complete Analysis
Integrity and Authenticity in Cryptography

In cybersecurity, cryptography provides the tools that enforce both integrity and authenticity, not just through theory, but through mathematically proven methods that attackers cannot easily bypass.
How Cryptography Ensures Integrity
To guarantee integrity, cryptographic algorithms use hash functions. A hash is a fixed-length digital fingerprint of data. Even the slightest change in the original data will result in a completely different hash.
- Example tools: SHA-256, MD5 (legacy), HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code).
How Cryptography Ensures Authenticity
For authenticity, cryptography employs digital signatures and public key infrastructure (PKI). These tools verify that data or files come from a known, trusted sender and haven’t been modified since being signed.
- Process: The sender signs data with their private key, and recipients verify the signature using the public key.
- Example tools: X.509 digital certificates, PGP/GPG, Code Signing Certificates.
Dual Protection: Integrity + Authenticity
- Digital Signatures offer integrity (data wasn’t altered) and authenticity (data is from the trusted sender) in one process.
- This is why integrity and authenticity in cryptography are inseparable in high-security environments such as banking, healthcare, and government systems.
Non-Repudiation Through Cryptography
When a file or message is digitally signed, the sender cannot deny sending it. This is non repudiation in cyber security, a legal and technical guarantee that supports trust, accountability, and compliance.
Cryptography, when properly implemented, ensures that what you see is what was sent, and who sent it is who they claim to be.
MORE: Risk Avoidance Cybersecurity: 2025 Strategies to Eliminate Threats
File Integrity vs File Authenticity in Practice
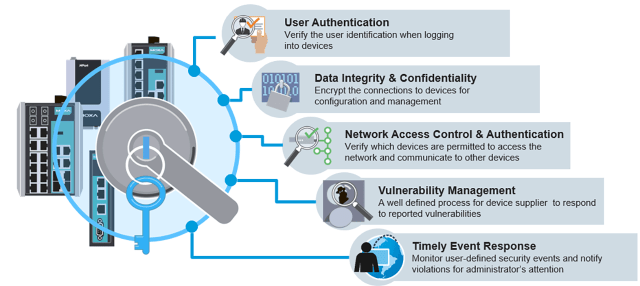
Understanding the practical difference between file integrity and file authenticity is crucial, especially in everyday cybersecurity operations where verifying files, software, and data is routine.
File Integrity in Practice
File integrity means the content of a file has not been altered, corrupted, or tampered with.
- Example: When downloading software, users often see a SHA-256 hash provided. After downloading, the user can hash the file and compare it to the original. If they match, integrity is intact.
- Tools used: File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) software, hash generators, and comparison tools.
File Authenticity in Practice
File authenticity confirms the file originates from a verified and trusted source, and hasn’t been faked or spoofed.
- Example: A code-signed software installer shows it was created by Microsoft. The digital certificate attached proves its authenticity, assuring users it’s safe to install.
- Tools used: Code signing certificates, X.509 certificates, PGP signatures.
Why Authenticity Matters More in Modern Attacks
- In software supply chain attacks, hackers insert malicious code into legitimate software. If authenticity isn’t verified, the user may unknowingly install malware.
- Without digital signatures, even files with correct hashes can be dangerous if the source is untrusted.
Combined Protection
Integrity ensures the file is unchanged. Authenticity ensures it’s from a valid source.
This dual verification blocks attackers from distributing harmful software or data by simply mimicking file names or formats.
For complete cybersecurity, data authenticity vs integrity isn’t an either/or; both must work together.
ALSO: FIA vs GRC: Key Differences, Salaries & Real-World Examples
CIA Triad Revisited: Where Do Authenticity and Integrity Fit?

The CIA Triad, Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability, is the foundational model for cybersecurity. It helps professionals prioritize protections for data and systems. Let’s focus on how authenticity and integrity fit into this framework.
Integrity in the CIA Triad
Integrity is one of the three pillars. It ensures that data remains accurate, consistent, and free from unauthorized modification.
- Example: Financial systems rely on integrity to avoid errors in transactions or reporting.
- Without integrity, decisions based on altered data can lead to major security breaches or legal violations.
Where Does Authenticity Fit?
Traditionally, authenticity was seen as part of integrity, but this view is changing. In practice, authenticity supports integrity by verifying the source of data.
- New models are now expanding the triad into CIANA: Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability, Non-repudiation, and Authenticity.
Authenticity’s Role in Strengthening the Triad
- Authenticity ensures trust in identity, crucial for access control, secure communication, and safe software deployment.
- Without authenticity, integrity can be compromised, as attackers can introduce legitimate-looking, yet malicious, data.
Authenticity vs Integrity Cybersecurity CIA Triad Example
- A file downloaded from a bank’s official site (authentic + integral) is safe.
- A file downloaded from a spoofed website (not authentic), even if unaltered (integrity intact), poses a serious risk.
Both authenticity and integrity are now recognized as core components of digital trust, essential for cyber resilience, especially in fields like finance, healthcare, and government.
SEE: LLM AI Cybersecurity & Governance Checklist: A Practical Guide
Why Both Matter: Real-World Risks of Overlooking Either
In cybersecurity, neglecting either integrity or authenticity can open the door to costly attacks, compliance failures, and loss of trust. Let’s break down the risks and why both are essential.
When Integrity Fails
- Risk: Data becomes inaccurate or corrupted, leading to faulty decisions or system failures.
- Example: A hospital’s patient records are altered due to a malware infection. Even minor changes could result in incorrect treatment.
- Impact: Legal liabilities, financial penalties, and compromised safety.
When Authenticity Fails
- Risk: Attackers impersonate trusted sources, delivering malicious files or gaining unauthorized access.
- Example: In a supply chain attack, hackers sign malware with fake credentials, and users unknowingly install harmful software.
- Impact: Data breaches, reputational damage, and potential system takeovers.
Compliance and Regulatory Pressure
- Many frameworks, ISO 27001, NIST, HIPAA, require controls for both data authenticity and integrity.
- Failure to implement both can result in non-compliance, fines, and loss of certifications.
Cyber Resilience and Zero Trust
- Zero Trust security models rely heavily on verifying both the integrity and authenticity of every user, device, and piece of data.
- In this approach, nothing is trusted by default, making continuous verification essential for security.
Bottom Line
Overlooking integrity leads to data you can’t rely on. Overlooking authenticity leads to data you can’t trust the source of.
Both are required for a secure, resilient, and trustworthy digital environment.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is about locking down data and ensuring that it’s accurate and comes from a trusted source. That’s where integrity and authenticity come in. Integrity guarantees that your data remains unchanged and reliable. In comparison, authenticity confirms that your data or system interactions are with verified identities.
Together, they form a complete defense against data tampering, impersonation, and sophisticated cyber threats. In a world where supply chain attacks, spoofed software, and data manipulation are rising, relying on one without the other is a security gap you can’t afford.
Whether you’re a business leader, IT professional, or compliance officer, now’s the time to evaluate your systems:
- Are you using cryptographic tools for both integrity and authenticity?
- Are your files digitally signed and monitored for unauthorized changes?
- Are you meeting compliance requirements that demand both?
In cybersecurity, trust is everything, and it’s built on the solid foundation of authenticity and integrity.
FAQ
Is authentication part of integrity?
No, authentication is not part of integrity; it is part of authenticity.
Authentication verifies who someone is (e.g., using passwords, biometrics, or two-factor authentication), while integrity ensures that data has not been altered. However, both work together to maintain trust in cybersecurity systems. Integrity ensures unchanged data, while authentication ensures trusted access.
What is two person integrity in cyber security?
Two-Person Integrity (TPI) is a security control requiring two authorized individuals to perform or approve certain critical tasks or access sensitive information.
Purpose: Prevent unauthorized actions or fraud by enforcing shared responsibility.
Common in: Military, nuclear operations, and high-security environments.
Example: Launching a missile requires two officers to turn keys simultaneously; in cybersecurity, accessing a sensitive server may require two separate logins or approvals.
What are the two concepts of integrity?
The two main concepts of integrity in cybersecurity are:
Data Integrity Ensures that information is accurate, complete, and unaltered from its original state.
Maintains trustworthiness of data during storage, processing, and transfer.
System Integrity Ensures that IT systems function as intended and are free from unauthorized alterations or malware.
Focuses on the stability and security of software, hardware, and configurations.
Together, these ensure that both the data and the systems handling it remain secure.
Who is responsible for data integrity?
Everyone in an organization shares responsibility for data integrity, but specific roles include:
Data Owners: Define data accuracy standards and ensure proper handling.
IT Security Teams: Implement technical controls like access controls, encryption, and monitoring tools.
Compliance Officers: Ensure adherence to regulatory standards for data integrity (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR).
End Users: Follow data handling procedures and report anomalies.
Maintaining data integrity is a shared responsibility, but leadership must ensure policies, training, and tools are in place to support it.

