What Is the First Step in Creating Cybersecurity Controls?
Cybersecurity controls are essential in safeguarding organizations from the ever-evolving threats posed by malicious actors. From protecting sensitive data to ensuring uninterrupted operations, these controls form the backbone of a secure digital environment.
However, implementing cybersecurity controls without a clear plan can lead to inefficiencies and overlooked vulnerabilities.
The first step in creating effective cybersecurity controls is foundational to the success of the entire framework. Without it, organizations may struggle to align their controls with business goals, prioritize risks, or protect their most critical assets.
This article explores the critical importance of starting with a strong risk management regime.
It answers questions like “What is the first step in creating cybersecurity controls qui?” and “When implementing a control framework, what is an important first step?” It will also provide insights for those looking to build their cybersecurity knowledge step-by-step, including beginners seeking practical guidance.

RELATED: Can You Get into Cybersecurity with a Computer Science Degree?
What Are Cybersecurity Controls?
Cybersecurity controls are measures and mechanisms designed to protect systems, networks, and data from threats. These controls form the foundation of an organization’s defense strategy, helping to manage risks, mitigate vulnerabilities, and prevent unauthorized access.
There are four primary types of cybersecurity controls, each addressing different aspects of security:
- Administrative Controls: Policies and procedures that guide how security is managed, such as employee training, incident response plans, and compliance measures.
- Physical Controls: Security measures that restrict physical access, such as surveillance cameras, access badges, and secure server rooms.
- Technical Controls: Technology-driven protections like firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication.
- Operational Controls: Day-to-day processes like monitoring logs, conducting audits, and enforcing baseline security practices.
These controls work in tandem to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, aligning with the core principles of cybersecurity. For beginners wondering “What are the 4 types of security controls?”, understanding these categories is essential to grasping the basics.
By integrating examples such as intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and secure access policies, organizations can address potential risks systematically. As we move further, we’ll explore how defining and implementing these controls starts with a vital first step, establishing a risk management regime.
ALSO SEE: What Is the First Step in Creating Cybersecurity Controls
Cybersecurity Basics for Beginners

For those new to cybersecurity, understanding the basics is a crucial starting point. Cybersecurity involves protecting digital assets, such as data, systems, and networks, from threats like malware, phishing, and unauthorized access.
However, the complexity of modern technology means that effective protection requires more than just strong passwords or antivirus software.
Cybersecurity is built around three core principles, often referred to as the CIA triad:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals.
- Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and reliability of data by preventing unauthorized modifications.
- Availability: Guaranteeing that systems and data are accessible to authorized users whenever needed.
For beginners, resources like Cybersecurity for Beginners PDFs can provide step-by-step guidance to understanding these principles and how they tie into broader security practices. Additionally, concepts such as creating secure baselines, managing access controls, and monitoring for unusual activity are fundamental to establishing a strong cybersecurity posture.
As organizations aim to build their control frameworks, knowing where to begin is critical. This brings us to the question: “When implementing a control framework, what is an important first step?” The answer lies in establishing a robust risk management regime—a topic we will explore in the next section.
READ MORE: Difference Between Risk Assessment and Risk Management
Why Establishing a Risk Management Regime Is the First Step

When implementing a control framework, what is an important first step? The answer lies in establishing a risk management regime.
This foundational process ensures that cybersecurity controls are not only effective but also aligned with an organization’s specific needs and objectives. Without this step, organizations risk implementing controls that fail to address their most critical vulnerabilities.
A risk management regime involves systematically identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks. It begins by evaluating assets such as data, systems, and networks, and understanding their value to the organization. Next, it identifies potential threats; such as malware, insider threats, or phishing attacks; and vulnerabilities, such as outdated software or weak access controls.
This step is critical because it provides the organization with a clear understanding of its risk landscape. For example, a business handling sensitive customer data might prioritize encryption and access controls, while a manufacturing company might focus on securing operational systems against disruption.
By defining these priorities early, organizations can tailor their cybersecurity controls accordingly.
The importance of this step is further highlighted by frameworks like ISO 27001 and NIST, which emphasize risk assessments as a foundational element of cybersecurity. For beginners looking to understand “how to learn cyber security step-by-step,” mastering this process is essential for building a strong control framework.
As we move forward, we’ll break down the key components of a risk management regime and how it ties into effective cybersecurity.
Key Components of a Risk Management Regime
Establishing a risk management regime is a structured process that lays the groundwork for creating cybersecurity controls. It involves several critical components, each contributing to a comprehensive understanding of an organization’s risk landscape and guiding the implementation of effective controls. Below are the key elements of this process:
1. Defining Objectives
Before implementing any cybersecurity controls, organizations must clearly define their goals. Is the primary objective to prevent data breaches, comply with regulations, or protect critical assets from malicious actors?
By setting specific objectives, organizations can ensure their cybersecurity framework aligns with their business priorities. This step addresses the question: “When implementing a control framework, what is an important first step?”
2. Asset Identification and Classification
Understanding what needs to be protected is fundamental. Organizations should identify all assets, including sensitive data, hardware, software, and networks, and classify them based on their value and criticality. For example:
- High-value assets: Customer data or intellectual property.
- Medium-value assets: Internal communications or process documents.
This classification helps prioritize efforts, ensuring that the most critical assets are protected first.
3. Threat and Vulnerability Assessment
Once assets are identified, organizations must assess the potential threats and vulnerabilities associated with them. Threats could include external actors like hackers or internal risks like negligent employees. Vulnerabilities might be outdated software, weak access controls, or unsecured network configurations.
By understanding these factors, organizations can answer key questions such as:
- What are the main risks to sensitive data?
- How could attackers exploit vulnerabilities?
- Which systems or processes require immediate attention?
4. Establishing Baselines
To measure and monitor risks effectively, organizations must establish a secure baseline. This involves documenting the normal behavior of systems, networks, and user activities to identify anomalies or deviations that might signal a security breach.
Tools like IBM Security Analytics can assist in creating baselines by collecting and analyzing data from various sources. Establishing baselines not only supports the development of cybersecurity controls but also helps in ongoing monitoring and incident response.
By following these steps, organizations can create a risk management regime that provides a strong foundation for their cybersecurity strategy. This process not only guides the implementation of controls but also ensures they are targeted, efficient, and aligned with business goals.
SEE ALSO: Ransomware Attack Johnson Controls: A Comprehensive Review
Examples of Cybersecurity Controls for Beginners

For beginners stepping into cybersecurity, understanding the practical implementation of controls is essential. Cybersecurity controls are measures put in place to prevent, detect, or mitigate risks.
By familiarizing themselves with examples across different types of controls, individuals can grasp how these measures work in real-world scenarios. Below are examples categorized by the four primary types of security controls:
1. Administrative Controls
Administrative controls focus on policies, procedures, and training that establish the foundation for security practices. Examples include:
- User Education: Training employees to recognize phishing emails or use strong passwords.
- Incident Response Plans: Guidelines for responding to data breaches or system failures.
- Compliance Measures: Ensuring adherence to regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
2. Physical Controls
Physical controls protect hardware and infrastructure from unauthorized access. Examples include:
- CCTV Cameras: Monitoring access points to detect unauthorized entries.
- Access Badges: Restricting entry to server rooms and other secure areas.
- Locks and Fencing: Physically safeguarding critical infrastructure.
3. Technical Controls
Technical controls are technology-driven measures that secure data, systems, and networks. These controls often form the backbone of a cybersecurity framework and include:
- Firewalls: Blocking unauthorized network traffic.
- Encryption: Protecting sensitive data in transit and at rest.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitoring network activity to identify suspicious behavior.
4. Operational Controls
Operational controls are processes carried out daily to maintain security. Examples include:
- Log Monitoring: Regularly reviewing logs to detect unusual activity.
- Penetration Testing: Simulating attacks to identify vulnerabilities.
- Regular Software Updates: Ensuring systems are patched against known threats.
These examples serve as practical tools for organizations and beginners alike. Understanding the application of controls provides clarity on “Cybersecurity controls examples” and highlights their relevance to overall risk management.
By starting with beginner-friendly controls such as strong passwords, encryption, and firewalls, even those new to cybersecurity can make significant strides in securing their digital environment.
MORE: Risk Management Jobs and Salaries
The Role of Technical Controls in Cybersecurity

Technical controls are at the heart of any cybersecurity framework, providing the tools and technologies that secure systems, networks, and data. These controls are essential for automating security processes, limiting access to sensitive information, and detecting malicious activity.
For organizations and beginners alike, understanding the importance of technical controls is crucial when building a robust cybersecurity posture.
What Are Technical Controls?
Technical controls, also known as logical controls, are mechanisms that protect the digital aspects of an organization. Unlike administrative or physical controls, technical controls rely on software and hardware solutions to secure data and systems. They are often implemented after conducting a risk assessment to address specific vulnerabilities.
Examples of technical controls include:
- Firewalls: Acting as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks, firewalls prevent unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Ensuring that sensitive data is unreadable to anyone without the proper decryption key.
- Endpoint Protection Software: Tools like antivirus and anti-malware programs that secure devices from threats.
- Access Control Systems: Tools like role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) that limit user access to sensitive resources.
Why Are Technical Controls Critical?
Technical controls play a dual role in both prevention and detection:
- Preventing Threats: By blocking unauthorized users, filtering harmful traffic, and securing data transmissions, technical controls minimize entry points for cyberattacks.
- Detecting Threats: Tools like intrusion detection systems (IDS) and monitoring software help organizations identify suspicious activities before they escalate into serious incidents.
For example, multi-factor authentication (MFA) prevents attackers from accessing systems even if they have a user’s password, while intrusion detection systems alert security teams about potential breaches.
How Beginners Can Learn About Technical Controls
Understanding technical controls is a key step for those asking, “How to learn cybersecurity step-by-step?” Beginners can explore resources like Cybersecurity for Beginners PDFs to gain insights into practical applications of technical controls. Hands-on practice with tools like firewalls, encryption software, and monitoring solutions can further solidify their knowledge.
Technical controls are indispensable for safeguarding an organization’s digital environment. From securing sensitive data to detecting anomalies in real time, these controls form the backbone of a cybersecurity framework. As we continue, we’ll explore common mistakes organizations make when establishing cybersecurity controls.
READ: What Is Vendor Risk Management (VRM) & Vendor Risk?
Common Mistakes When Establishing Cybersecurity Controls
While implementing cybersecurity controls is essential, mistakes during the process can lead to gaps in security, making an organization vulnerable to threats. Understanding these common pitfalls ensures that organizations and beginners alike can avoid errors and create a more effective control framework. Below are some of the most frequent mistakes encountered:
1. Skipping the Risk Management Step
One of the most critical mistakes is bypassing the initial step of establishing a risk management regime. When organizations jump straight into implementing technical solutions, such as firewalls or antivirus software, without understanding their specific risks, they may misallocate resources or fail to address critical vulnerabilities.
Answering “What is the first step in creating cybersecurity controls qui?” is essential—beginning with a thorough assessment of assets, threats, and vulnerabilities.
2. Failing to Align Controls with Business Objectives
Cybersecurity is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Controls need to align with an organization’s specific business goals and priorities.
For instance, a healthcare organization might prioritize data encryption to comply with HIPAA regulations, while a retail business might focus on securing customer payment data. Without this alignment, controls may fail to protect what matters most.
3. Ignoring User Education and Awareness
Cybersecurity is as much about people as it is about technology. Overlooking user education; such as training employees to identify phishing attempts or practice good password hygiene; can render even the most advanced technical controls ineffective. Educating users about cybersecurity basics for beginners helps build a human layer of defense against cyber threats.
4. Implementing Controls Without Ongoing Monitoring
Another common oversight is neglecting to establish continuous monitoring processes. Cyber threats evolve rapidly, and controls that were effective yesterday may not work tomorrow. Without regular monitoring and updates, organizations risk leaving vulnerabilities unaddressed.
Tools like IBM Security Analytics and other monitoring solutions can help organizations keep their defenses up to date.
5. Overcomplicating the Framework
Introducing overly complex controls, especially for small businesses or beginners, can lead to non-compliance or confusion. Employees may circumvent controls that feel too restrictive, weakening the overall security posture. Controls should be tailored to the organization’s size, resources, and risk appetite.
6. Failing to Regularly Review and Test Controls
Many organizations implement controls and then fail to review or test them regularly. Controls like access permissions, software patches, and intrusion detection systems require consistent evaluation to ensure they are functioning as intended. Regular penetration testing and audits help identify weaknesses and improve defenses.
By recognizing these common mistakes, organizations can create a stronger cybersecurity framework. Avoiding these pitfalls ensures that controls are not only implemented effectively but also remain relevant as threats evolve.
SEE: Risk Analysis in Cyber Security
How to Learn Cybersecurity Step-by-Step
For beginners aiming to build a strong foundation in cybersecurity, adopting a step-by-step approach is key. Cybersecurity is a broad field that requires understanding core concepts, practical skills, and real-world applications. Whether you’re an aspiring professional or someone looking to secure personal systems, the following steps offer a clear path to mastery.
1. Start with Cybersecurity Basics for Beginners
Begin by familiarizing yourself with foundational concepts like the CIA triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability). Understanding these principles provides a lens through which cybersecurity strategies and controls are designed.
Resources such as Cybersecurity for Beginners PDFs are great starting points, as they often simplify complex concepts for new learners.
2. Understand the Importance of Risk Management
As highlighted earlier, the first step in creating cybersecurity controls is establishing a risk management regime. Learn to identify assets, assess threats, and evaluate vulnerabilities. This foundational knowledge is crucial in answering questions like “What is the first step in creating cybersecurity controls qui?” and is integral to implementing effective controls.
3. Explore Cybersecurity Control Types
Understanding the four types of security controls, administrative, physical, technical, and operational, is essential. Delve deeper into:
- Technical Controls: Study tools like firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems.
- Operational Controls: Learn about processes such as log monitoring, regular audits, and patch management.
This step will help you grasp cybersecurity controls examples and their application in real-world scenarios.
4. Gain Hands-On Experience with Tools
Practical experience is vital. Begin with free tools like Wireshark for network monitoring, Snort for intrusion detection, or even configuring firewalls on personal devices. Many online platforms offer interactive labs and virtual environments where you can safely practice cybersecurity skills.
5. Study Security Frameworks
Familiarize yourself with widely used cybersecurity frameworks like NIST Cybersecurity Framework and ISO 27001. These frameworks provide a structured approach to building and maintaining security programs and highlight how to implement controls step-by-step.
6. Participate in Cybersecurity Communities
Joining forums, attending webinars, and participating in challenges such as capture-the-flag (CTF) events can accelerate your learning. Communities allow you to engage with experienced professionals and stay updated on the latest threats and solutions.
7. Build Knowledge Through Certifications
Consider beginner-friendly certifications such as:
- CompTIA Security+: Covers fundamental cybersecurity principles.
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA): Focuses on governance and risk management.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): Introduces hacking techniques and defense mechanisms.
These certifications validate your knowledge and provide structured learning pathways.
8. Monitor Progress and Stay Updated
Cybersecurity is an ever-evolving field, so staying updated on new threats, tools, and best practices is critical. Regularly revisit your learning goals and adapt to emerging trends.
By following this step-by-step process, beginners can confidently transition from understanding cybersecurity basics to implementing effective controls. Whether you’re securing personal devices or contributing to an organization’s cybersecurity framework, this roadmap ensures steady progress.
Conclusion
The first step in creating effective cybersecurity controls is establishing a robust risk management regime. This foundational process allows organizations to identify their assets, assess vulnerabilities, and prioritize threats before implementing tailored controls.
Without this critical step, cybersecurity efforts can become fragmented, misaligned, and ineffective against evolving threats.
Cybersecurity is not just about technology but also about aligning controls with business objectives, educating users, and maintaining vigilance through ongoing monitoring. Beginners looking to build their knowledge step-by-step should focus on understanding core principles, exploring practical tools, and mastering control frameworks.
Resources like Cybersecurity for Beginners PDFs and certifications provide an accessible entry point to the field.
By avoiding common mistakes such as skipping the risk assessment stage or overcomplicating controls, organizations can create a secure environment that protects critical assets and maintains trust. Cybersecurity is an ongoing effort, but starting with the right foundation ensures every subsequent step strengthens the overall defense.
The journey to mastering cybersecurity begins with the basics, whether you’re a beginner or a professional. Take the first step, stay committed, and build a security framework that not only meets today’s challenges but adapts to tomorrow’s threats.
FAQ
What is the first step for cyber security?
The first step for cybersecurity is establishing a risk management regime. This involves identifying assets, assessing potential threats, and analyzing vulnerabilities to prioritize risks. By understanding the organization’s specific risk landscape, you can implement tailored controls that protect critical systems and data while aligning with business objectives. A risk management regime forms the foundation for an effective cybersecurity framework.
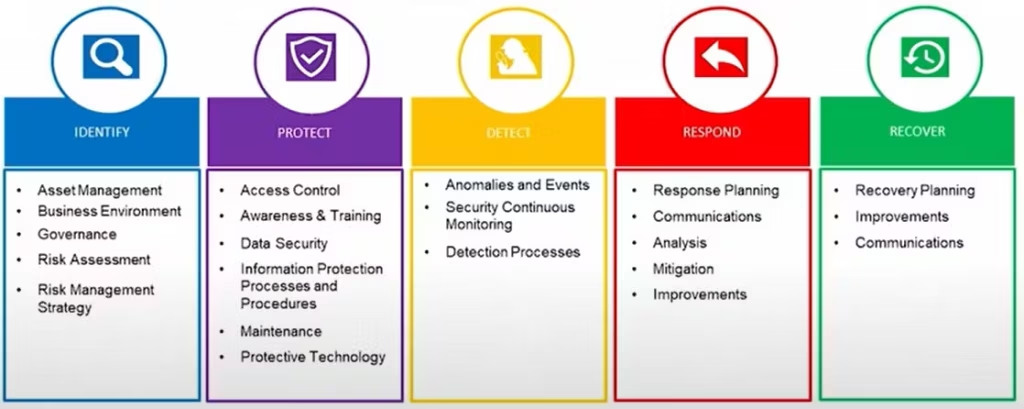
What are the 5 steps of cyber security?
The 5 steps of cybersecurity are typically aligned with frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and include:
Identify: Assess your assets, threats, and vulnerabilities to understand your risk landscape.
Protect: Implement security controls like firewalls, encryption, and access management to safeguard systems.
Detect: Deploy tools and processes to identify suspicious activities, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS).
Respond: Establish an incident response plan to contain and mitigate the impact of cyber threats.
Recover: Implement strategies for data recovery, system restoration, and lessons learned to improve future resilience.
What is the first rule of cybersecurity?
The first rule of cybersecurity is to know what you are protecting. This involves identifying and classifying assets; such as data, systems, and networks; and understanding their value to your organization.
Without knowing what needs protection, it is impossible to implement effective controls. This rule emphasizes the importance of visibility, awareness, and prioritization in cybersecurity efforts.
What are the five 5 steps of the cybersecurity lifecycle?
The cybersecurity lifecycle outlines a continuous process to manage and protect against cyber threats. The five steps are:
Identify: Determine critical assets, vulnerabilities, and risks to create a baseline.
Protect: Implement safeguards like secure configurations, technical controls, and user education to reduce risk.
Detect: Monitor systems and networks to identify anomalies or unauthorized activities.
Respond: Develop a response plan to manage and mitigate the impact of incidents.
Recover: Ensure systems and data can be restored to normal operations while improving the overall cybersecurity framework through lessons learned.
These steps reflect a proactive and cyclical approach to maintaining strong cybersecurity defenses.
If you’re ready to take the next step in your cybersecurity journey? You can do that with an expert beside you to guide you through without having to stress much. Schedule a one-on-one consultation with Tolulope Michael, a cybersecurity professional with over a decade of field experience. This will allow you to gain personalized insights and guidance tailored to your career goals.
Visit tolumichael.com now to book your session. This is your opportunity to embark on your cybersecurity career with confidence. Don’t miss out!

